Using the Debugger
What does Xcode do? Xcode includes everything developers need to create great applications for Mac, iPhone, iPad, Apple TV, and Apple Watch. Xcode provides developers a unified workflow for user interface design, coding, testing, and debugging. The Xcode IDE combined with the Swift programming language make developing apps easy and fun. Oct 23, 2018 In this tutorial, we will look at how you can use the XCode simulator to debug a web page. XCode is a free IDE available for Mac devices used for developing all kind of apps for Apple devices: iOS. I am debugging an iPhone app I'm writing in Xcode, but sometimes now the debugger (which is GDB) slows a lot (doing a step-by-step debugging) and becomes unresponsive sometimes (the icons for stepping-in, stepping-over, stepping-out are not clickable), after sometimes it gets back to normal and continues and other times it stay like that forever or a message appears in console: 'Timed out' (or. I have an iPhone and necessary certificates also, but don't know how to debug an application using xCode to iPhone. I have all these. I have Mac Mini and iPhone 3g, but I don't know how to use all these certificates. I want to debug an application - having shake handling code. That I can't debug on simulator. Sep 21, 2016 Instead, try opening the Watch app on your iPhone (not your app - the Apple's 'Watch' app). This usually, for whatever reason, makes my app launch on the watch, and it's ready to output debug. Or at least it used to output debug in XCode 7.x. In Xcode 8, it just stopped doing this.
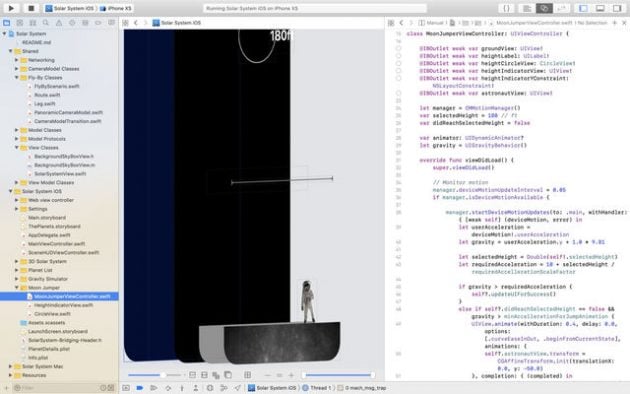
After you click the Run button in the workspace toolbar and your app builds successfully, Xcode runs your app and starts a debugging session. You can debug your app directly within the source editor with graphical tools such as data tips and Quick Look for the value of variables.
The debug area and the debug navigator let you inspect the current state of your running app and control its execution.
Creating a quality app requires that you minimize your app’s impact on your users’ systems. Use the debug gauges in the debug navigator to gain insight into your app’s resource consumption, and when you spot a problem, use Instruments to measure and analyze your app’s performance. Use the energy guides to minimize your impact on battery life. For more information, see Energy Efficiency Guide for iOS Apps and Energy Efficiency Guide for Mac Apps.
If you are developing an iOS or watchOS app, use Simulator to find major problems during design and early testing.
You can configure Xcode to help you focus on your debugging tasks. For example, when your code hits a breakpoint, you can make Xcode automatically play an alert sound and create a window tab named Debug, where Xcode displays the debug area, the debug navigator, and your code at the breakpoint.
Controlling Execution
Xcode lets you step through your code line by line to view your program’s state at a particular stage of execution. Use the debug area to control the execution of your code, view program variables and registers, view its console output, and interact with the debugger. You can also use the debug area to navigate the OpenGL calls that render a frame and to view the rendering-state information at a particular call.
Display the debug area by clicking the center button () in the view selector in the workspace window toolbar.
You can suspend the execution of your app by clicking the pause button (which toggles between to pause and to continue) in the debug area toolbar. To set a breakpoint, open a source code file and click the gutter next to the line where you want execution to pause. A blue arrow () in the gutter indicates the breakpoint. For more information on breakpoints, including how to set breakpoint actions and the different kinds of breakpoints, see Xcode Help.
When your app is paused, the currently executing line of code is highlighted in green. You can step through execution of your code using the Step Over (), Step Into (), and Step Out () buttons located in the bar at the top of the debug area. Step over will execute the current line of code, including any methods. If the current line of code calls a method, step into starts execution at the current line, and then stops when it reaches the first line of the called method. Step out executes the rest of the current method or function.
Viewing State Information
When execution pauses, the debug navigator opens to display a stack trace. Select an item in the debug navigator to view information about the item in the editor area and in the debug area. As you debug, expand or collapse threads to show or hide stack frames.
Hover over any variable in the source code editor to see a data tip displaying the value for the variable. Click the Inspector icon () next to the variable to print the Objective-C description of the object to the debug area console and to display that description in an additional popover.
Click the Quick Look icon () to see a graphical display of the variable’s contents. You can implement a custom Quick Look display for your own objects. See Quick Look for Custom Types in the Xcode Debugger.
Finding Memory Corruption
Memory corruption crashes can be hard to reproduce and even harder to find. Address sanitizer adds instrumentation to your app that enables Xcode to stop your app where the corruption happens. Address sanitizer finds problems such as accessing deallocated pointers, buffer overflow and underflow of the heap and stack, and other memory issues.
Test Xcode On Iphone
To use address sanitizer, enable it in the debug scheme for your target, then run and use the app. Xcode monitors memory use and stops your app on the line of code causing the problem and opens the debugger. Use the debugger to isolate the cause.
For more information on using address sanitizer, see Using the Address Sanitizer
Xcode Debug On Iphone
Debugging Metal
Metal takes full advantage of modern GPUs so your apps can give the best user experience. You can use Metal to accelerate both graphics and computation, all using a streamlined API. For information on debugging Metal, see Metal Tips and Techniques. For general information, see Metal for Developers on the developer website and Metal Programming Guide.
Debugging OpenGL
When you build and run an OpenGL ES app on a connected device, the debug area toolbar includes a Frame Capture button (). Click that button to capture a frame. You can use OpenGL ES frame capture to:
Inspect OpenGL ES state information
Introspect OpenGL ES objects such as view textures and shaders
Step through the state calls that precede each draw call and watch the changes with each call
Step through draw calls to see exactly how the image is constructed
See in the assistant editor which objects are used by each draw call
Edit shaders to see the effect upon your app
The screenshot shows the use of the debugger to view components of a rendered frame. The debug navigator on the left shows parts of the rendering tree, and the main debug view shows the color and depth sources for the rendered frame as well as other image sources.
For more help debugging OpenGL ES, see related items in Xcode Help and Xcode Help.
Copyright © 2018 Apple Inc. All rights reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Updated: 2016-10-27